Carpal tunnel syndrome can have a very significant impact on a person’s life. The wrist pain, the muscle weakness, the numbness in the hands, particularly the fingers, and the potential loss of earnings from being unable to do your job, all add up to a feeling that a sufferer’s quality of life is less than it should be. Although a painful and worrying thing to endure, CTS can be treated with modern medicines, changes of habits and simple surgery if required. Please read on to learn more about the symptoms and treatments.
Early Signs OF CTS
CTS often affects your dexterity, that is, the ability to use your hands effectively to carry out certain tasks. You may find you often drop things, have difficulty using a keyboard or fastening the buttons on clothing.
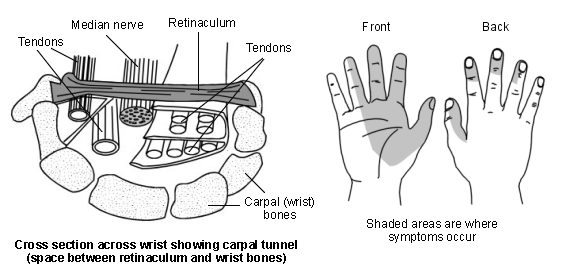
Other symptoms Symptoms Of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome include tingling, numbness and pain in one or both hands. The symptoms of CTS usually occur in the thumb, the index finger, the middle finger and half of the ring finger, however, the tingling and pain can sometimes be felt outside of these areas and tend to get worse as time passes.
Dealing With The Initial Symptoms
There are things you can do should you begin to feel any of the symptoms, try and adjust the position of your wrists if you have a job where repetition is an issue. Typists, for example, who have a tendency to suffer from RSI (repetitive strain injury), can use an ergonomic keyboard, take a few breaks to stretch the wrists, and do a few hand exercises to keep things flexible. Over the counter painkillers can help alleviate the pain, and if it starts to get really uncomfortable during the night, wearing a wrist splint to keep the wrist in a neutral position can help.
Where Is The Carpal Tunnel?
There are eight small bones called carpal bones in the wrist, a ligament lies across the front of the wrist. Between the ligament and the carpal bones is a space called the carpal tunnel. The tendons that attach the forearm muscles to the fingers pass through the carpal tunnel. One of the main nerves (median) to the hand also goes through this tunnel before dividing into smaller branches in the palm. The median nerve gives feeling to the thumb, index and middle fingers as well as half of the ring finger. It also controls the movement of the small muscles at the base of the thumb. Sometimes, thickening from irritated tendons or other swelling narrows the tunnel and causes the median nerve to be compressed.
Diagnosis Of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
If you feel that you are suffering from any symptoms as outlined above, it is important to get an early diagnosis. A physician will examine the hands, arms, shoulders, and neck to help determine if the symptoms are related to daily activities, to an underlying disorder, or in fact to carpal tunnel syndrome itself. The wrist is examined for tenderness, swelling, warmth, and discoloration. Each finger will be tested for sensation, and the muscles at the base of the hand will be examined for strength and signs of atrophy (cell degeneration). Other tests may be carried out in order to spot diabetes, fractures or arthritis.
Treating Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Early treatment of diagnosed cases of CTS is vital in order to avoid permanent damage to the median nerve. If there are any reasons, any underlying issues, (health or occupational) that may have caused the CTS then these should be treated.
If caught early enough, or, in less severe cases then surgery can be avoided. This may involve changing the activities that caused the problems in the first place, wearing a wrist splint, the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve the pain and reduce any inflammation. Note: Sometimes seen as a not-so-common side effect of pregnancy, CTS usually disappears without treatment within a year.
If you have had carpal Tunnel Syndrome for a long time, or if there is a risk of nerve damage then surgery may be your best option.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Surgery
Nowadays surgery for CTS is a simple procedure and not one that should cause any concern, First, an incision is made in the middle of the base of the hand just beyond the wrist skin crease. Once under the skin, the carpal ligament can be divided to allow the carpal tunnel to spring open, making space for the median nerve and restoring blood flow in its artery. The painful tingling in the fingers stops immediately, though some painkillers will be needed for a day or two after surgery. The skin is usually well healed within two weeks, allowing people to start light work again very quickly and if the job entails, they can start back to doing heavy work in around 4-6 weeks.
For any advice on this or any other cosmetic procedure then please feel free to contact us on 09 522 0652 or find details of your nearest Plastic Surgical Centre for a consultation.
See more information about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome